Thursday, November 30, 2006
Wednesday, November 29, 2006
'Microsoft.VisualStudio.Tools.Applications.Adapter, Version=8.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=b03f5f7f11d50a3a'

When i got this error i tried to uninstall the Visual Studio 2005 SDK Feb release from my system. Now the problem get solved.

For more check out these articles.
http://msdn2.microsoft.com/en-us/library/zdc263t0.aspx
http://www.summsoft.com/blogs/garyvsta/default.aspx
Saturday, November 18, 2006
New Technology discussion group in MSN - Join Now
Join Now
http://groups.msn.com/DevelopersParadise
Thursday, November 16, 2006
Unsafe Code in C#
When and why should we need this unsafe or unmanaged code in .NET? The answer is if you want to access memory mapped devices or if you want to create an application that to interface with your operation system, while using pointer to increase your application performance, External functions, in some cases you might need to write an application that analyzes another application process and memory etc, we need this unmanaged code, it will be more advantageous when we use this in those situations.
Some of the main advantages about the unsafe code in .NET are performance and flexibility, compatibility like DLLImport, memory addresses.
Some of the notable disadvantages about the unmanaged code in .NET are Complex to implement in C#, you should be more careful while using pointers in .NET application, miss use of pointer will cause many problems like stack overflow, overwrite existing or other variables, unauthorized access to memory areas, simple mistake in using pointers might lead your application to crash randomly and unpredictably, using pointers will cause the code to fail in the .net type-safety checks.
Sample unmanaged code snippet:
DllImport("shell32.dll", SetLastError = true)]
extern public static bool
ShellExecuteEx(ref ShellExecuteInfo lpExecInfo);
public const uint SW_NORMAL = 1;
static void OpenAs(string file)
{
ShellExecuteInfo sei = new ShellExecuteInfo();
sei.Size = Marshal.SizeOf(sei);
sei.Verb = "openas";
sei.File = file;
sei.Show = SW_NORMAL;
if (!ShellExecuteEx(ref sei))
throw new System.ComponentModel.Win32Exception();
}
For more reference
Sunday, November 12, 2006
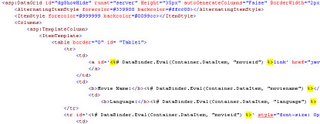
Show/Hide a row in ASP.NET DataGrid
Sample XML document structure:
<movies>
<movie movieid="1000">
</movies>
After populating the grid, my grid shows like this...
JavaScript to do Show/Hide in ASP.NET Datagrid:


Saturday, November 11, 2006
C# to VB.NET and VB.NET to C#
C# to VB.NET Links:
http://www.kamalpatel.net/ConvertCSharp2VB.aspx
VB.NET to C# Links:
http://www.carlosag.net/Tools/CodeTranslator/Default.aspx
http://www.developerfusion.co.uk/utilities/convertvbtocsharp.aspx
Tuesday, November 07, 2006
"LoaderLock was detected" Error when debugging my .NET DirectX code sample:
Check this original error message:
LoaderLock was detected
DLL 'C:\WINDOWS\assembly\GAC\Microsoft.DirectX\1.0.2902.0__31bf3856ad364e35\Microsoft.DirectX.dll' is attempting managed execution inside OS Loader lock. Do not attempt to run managed code inside a DllMain or image initialization function since doing so can cause the application to hang.
Managed Debugging Assistants is also referred as MDA, MDA work with the Common Language Runtime (CLR) to provide information on runtime state. They generate information about runtime events. Load Lock is one of the MDA available in .NET framwork, the code part which exist in all Managed DirectX 1.1 assemblies, is the reason to MDA firing. The most common failure when executing code inside the operating system's loader lock is that threads will deadlock when attempting to call other Win32 functions that also require the loader lock.
The only thing that seems to hold this situation is simply to turn off the MDA for LoaderLock, which is not recommended solution.
Global registry key which is used to turn on/off MDA.
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\.NETFramework]
"MDA"="1"
Better options to work around this problem are...
Look at the stack trace for the thread that has activated this MDA. The thread is attempting to illegally call into managed code while holding the operating system's loader lock. You will probably see a DLL's DllMain or equivalent entry point on the stack. The operating system's rules for what you can legally do from inside such an entry point are quite limited. These rules preclude any managed execution.
To go back to Visual Studio 2003 and .NET 1.1 . Else disable the loader lock Managed Debugging Assistants. Debug/Exceptions, Open the Managed Debugging Assistants tree node and uncheck Loader Lock. This setting is per solution so it will only affect this solution.
Tips:
In VS2005, go to the Debug->Exceptions menu. Within the Exceptions dialog expand the "Managed Debugging Assistants" node. Look for LoaderLock and uncheck the "Thrown" column.
Note: Do not disable all MDAs by setting MDA="0" in the registry as it causes problems.
Mixed managed/unmanaged C++ assemblies built for .NET Framework versions 1.0 or 1.1 generally attempt to execute managed code inside the loader lock unless special care has been taken. .NET 1.1 Managed DirectX assemblies when used with Visual Studio 2005 and .Net 2.0.
Learn About MDA:
Diagnosing Errors with Managed Debugging Assistants
Microsoft Helps related to this problem:
Managed Debug Assistants (MDAs) are cool.
Microsoft Visual Studio 2005 to debug a Microsoft Foundation Classes (MFC) class library application
Sunday, November 05, 2006
Using C#.NET play multimedia files - Using Multimedia Control Interface(MCI)
About Media Control Interface (MCI):
The Media Control Interface (MCI) provides standard commands for playing resource files. MCI's standard commands are a generic interface to almost all kind of multimedia devices. Media Control Interface provides applications with device-independent capabilities for controlling audio. MCI - High level multimedia control functions, Has commands common to all multimedia hardware. Possible since most use record/play metaphor Open a device for input or output If input, record; If output, play When done, close.
There are two different forms of MCI, one is Send command messages (like Windows messages) to MCI (need to include bit-encoded flags and C data structures) and another one is Send text strings to MCI Good for use from scripting languages with string functionality and simple to use MCI converts them to command messages.
Sending Strings to MCI:
error = mciSendString(sCmd , sRetStr, iReturn, hCallback);
· sCmd--themci command string (specifies command & device)
· sRetStr--return string buffer (NULL if none used)
· iReturn--size of return string buffer (0 if none used)
· hCallback--Handle to Callback window (NULL if none used)
– Returns 0 if command is successful, error code if not
· Can be used as a parameter to mciGetErrorString()
– Many command strings possible
– mciSendString, mciGetErrorString
– MCI Command Strings
For more details or help check the MSDN.
When Using Win32 Functions From .NET
Important note, MCI is not directly accessible from .NET, also mciSendString() is C++, not C#, but still you can use MCI and other Win32 API functions from .Net languages. The key is to use “Platform Invocation Services” “Interop Services” A generalized mechanism that allows calling functions that are imported from DLLs.
Must include: System.Runtime.InteropServices namespace; And then prefix any declarations of Win32 API functions to be used.
Example:
[DllImport("winmm.dll")]
private static extern long mciSendString(
string strCommand,
StringBuilder strReturn,
int iReturnLength,
IntPtr oCallback);
For MCI functions that DLL is winmm.dll, And then use equivalent .NET language data types for the parameters and for the type returned by the function.
Some of the disadvantages to be notes:
Code is no longer managed code and it’s no longer platform independent.
mciSendString() in .NET Unmanaged Code:
Corresponding C# parameter types would be:
– string, string, uint, intPtr
– In C# DWORD is implemented as an int
strCommand - Pointer to a null-terminated string that specifies an MCI command string.
strReturn - Pointer to a buffer that receives return information. If no return information is needed, this parameter can be null.
iReturnLength - Size, in characters, of the return buffer specified by the strReturn parameter. hwndCallback - Handle to a callback window if the "notify" flag was specified in the command string.
Some MCI Command String Commands:
· open -- initializes a multimedia device
· play– starts playing an open device
· stop -- stops playing from an open device
· record -- starts recording to a device
· seek -- move to a specified position on device
· save -- saves an MCI file
· close -- closes a device and associated resources
· set -- establish control settings for the device
· status -- returns information in 2nd parameter
However, most of these libraries are designed in such a way that they cannot be used to manipulate audio samples on the fly because they do not give you access to the actual sound data.
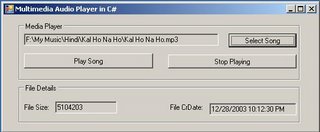
Here in this article i have covered some basics about the MCI in .NET. You can explore more in MSDN or in any other resource centre.
>>Download The Sample Code>>
ASP.NET MVC - Sport Facility Booking system
The project relies on some external service providers. Thus accessing them via their API requires authentication. An API Key need to be su...
-
The project relies on some external service providers. Thus accessing them via their API requires authentication. An API Key need to be su...
-
"The server is configured to use pass-through authentication with a built-in account to access the specified physical path. However, II...
-
Excellent outcome by some of the Microsoft Technology community influencers. CAML.NET IntelliSense for SharePoint To build a SharePoint feat...